With organizations increasingly shifting their workloads onto the public cloud (GCP, AWS, Azure, or Alibaba Cloud), security processes have to evolve to consider the change in the infrastructure environment. While the public cloud enables organizations to develop products at an unprecedented speed, it also brings about its own set of security issues.
Organizations will have to modify traditional vulnerability management processes to take into consideration the changes introduced by the public cloud. This includes understanding how the public cloud infrastructure works and adopting the customer’s portion of the shared responsibility model.
Cloud Vulnerability Management Processes
The Vulnerability Management Guidance Framework by Gartner lists Assess, Prioritize, Act, Re-assess, and Improve, as different sections. Public cloud providers, through their service offerings, introduce several tools and managed services that provide a layer of abstraction over the hardware they manage. Several stages of the vulnerability management process has to consider the use and impact of these tools and services.
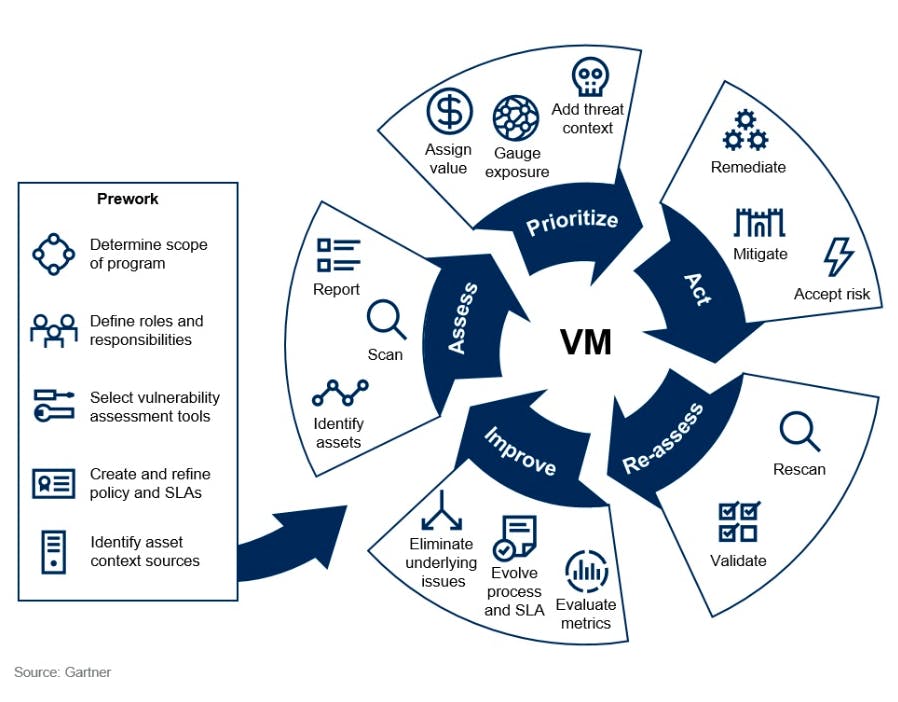
Vulnerability management guidance framework
1. Assess
Security threats such as misconfigurations and unauthorized access are the leading causes of cloud data breaches. These are also more rampant in workloads residing in the public cloud. This is partially due to the ease of use of public cloud infrastructure, which can be easily configured to allow public or cross-account access. This is made more challenging by the long list of managed services, each with its own access policy configurations. The list of security threats needs to expand to include the myriad of possible cloud misconfigurations.
Public cloud providers also provide managed services for audit logging, which includes API calls to their servers. These cloud API activities contain key information that could aid in detecting suspicious activities such as an IAM service account/user trying to delete production workloads. Traditional monitoring and alerting processes have to be updated to include the use of these audit logs.
2. Prioritize
As with all vulnerabilities, not all may be relevant or immediate for your organization. As proposed by Gartner, employing a risk-based approach to vulnerability management is a more sustainable approach.
Managed services for storage such as S3 are usually more relevant for organizations, given that misconfigurations can easily cause the data that is stored to be publicly accessible. Other managed services such as network access controls that control access to other resources are also more likely to be relevant. When prioritizing vulnerabilities, organizations should consider the implications of managed services.
Organizations should also keep in mind that public cloud providers implement security upgrades from time to time. If a vulnerability is of lower severity, waiting for the upgrade from the cloud provider can reduce implementation effort and cost. Examples include updated TLS standards or patch updates for database engine versions. Organizations should consider the public cloud provider’s security upgrade release cycles when prioritizing vulnerabilities.
Not all vulnerabilities are equally threatening when you consider the context. For example, vulnerabilities that have the highest impact on production systems should be prioritized, while others could be ignored if they have minimal impact or if there are workarounds. Organizations should classify vulnerabilities according to their priority.
Our Solution: Horangi Warden’s vulnerability management feature allows you to do just that - classify vulnerabilities or suppress them.
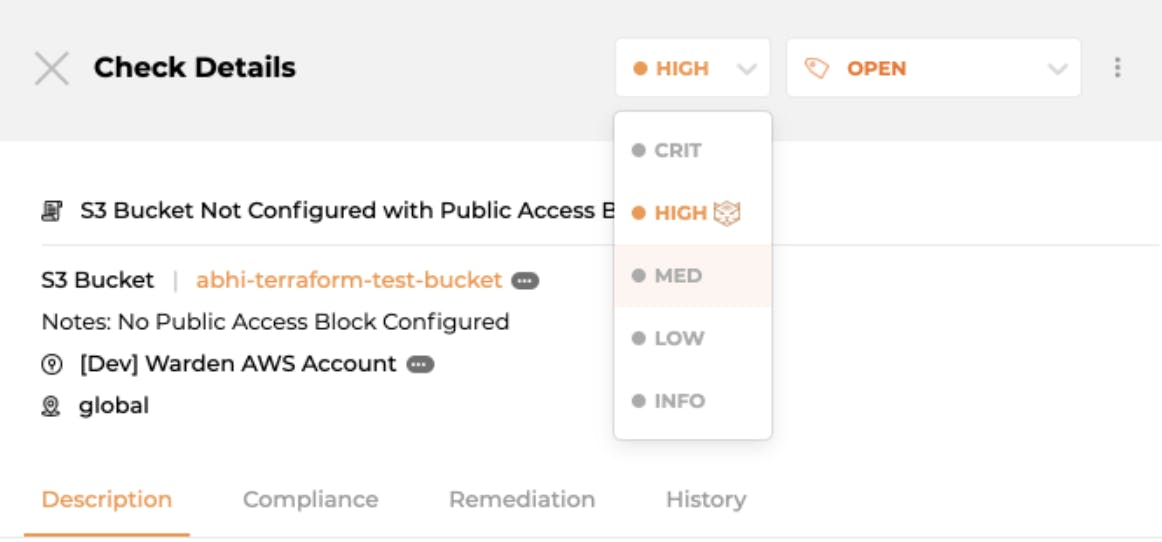
Assigning a new severity for a vulnerability in Warden
3. Act
Increasingly, organizations are using infrastructure as code (IAC) to provision infrastructure in public cloud environments. Modifying infrastructure code such as Terraform or CloudFormation will ensure that infrastructure vulnerabilities are fixed at build time. If the infrastructure vulnerability is critical, public cloud provider APIs can be used to fix them in real-time. These cloud tools should be considered as part of the toolkit for organizations to remediate vulnerabilities.
Our Solution: Horangi Warden’s One-Click Remediation feature allows users to fix infrastructure vulnerabilities from the user interface. Bulk remediation is also available for users to remediate multiple vulnerabilities at the same time.
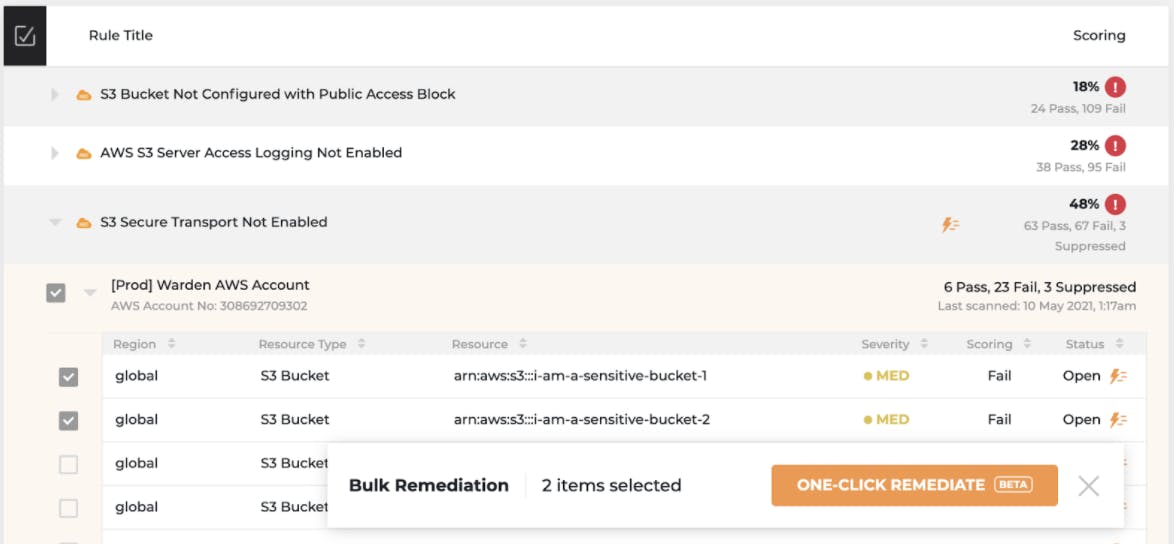
Executing bulk remediation on an S3 vulnerability in Warden
Cloud Breaches and Cloud Vulnerability Management
Two of the largest public cloud data breaches in recent years can be traced back to cloud misconfigurations. The Capital One data breach that compromised the personal data of 100 million customers was traced to an improperly configured AWS Web Application Firewall. The AutoClerk breach resulted in travel information of US military personnel being leaked and was caused by a publicly accessible ElasticSearch instance.
These misconfigurations could have been detected more effectively with an updated Vulnerability Management process that understands how the public cloud works.
Cloud Vulnerability Management Solutions
Utilizing a Cloud Vulnerability Management Solution allows organizations to offload the process of identifying threats to the solution provider. These solutions usually come with workflows for assessments, remediations, and reporting, providing a single pane glass view for the organization’s security posture.
Aside from third-party solutions, cloud providers themselves also provide support (Security Hub for AWS and Google Security Command Center for GCP). While these tools provide a baseline to work with, a dedicated third-party solution can provide a more fully-featured system that also streamlines the process for a multi-cloud environment.
Conclusion
While hosting workloads in the public cloud brings several benefits, organizations should not forget to evolve their Vulnerability Management processes to keep up with the change in the environment. A deep understanding of how the public cloud works goes a long way in shaping your organization’s security processes and in improving your security posture.
As a Cloud Security Posture Management tool, Horangi Warden provides hundreds of rules for cloud providers like AWS, GCP, Azure (coming soon), and Alibaba Cloud (coming soon) providing companies with the identification and assessment of their cloud vulnerabilities, while also providing the option for one-click remediation. This allows companies to focus on building their own products while maintaining their security posture. Get a free risk assessment to understand your cloud security posture with a Horangi specialist. Contact us today!